Cyber Briefing: 2025.04.16
In this edition, we cover Linux malware, Node.js attacks, embassy phishing campaigns, the 4chan breach, social media hacks, the MITRE CVE crisis, NSA claims, and a £100M phishing bust.
Listen to our podcast here!
Welcome to Cyber Briefing, the newsletter that informs you about the latest cybersecurity advisories, alerts, incidents and news every weekday.
First time seeing this?
👉 What's trending in cybersecurity today?
🚨 Cyber Alerts
1. UNC5174 Group Target Linux with VShell RAT
UNC5174, a China-linked threat actor, has been deploying a sophisticated campaign using the SNOWLIGHT malware and VShell RAT to target Linux and macOS systems. This group takes advantage of open-source tools, making their activities more difficult to trace and attribute. The SNOWLIGHT malware serves as a dropper for a fileless in-memory payload called VShell, enabling remote access for cybercriminals to execute arbitrary commands, upload files, and maintain persistence within compromised systems.
2. Hackers Use Node.js to Deliver Malware
Node.js is increasingly being exploited by cybercriminals to deliver advanced malware and steal sensitive data. Attackers use techniques like malvertising, embedding malicious code into legitimate software, and exploiting supply chain vulnerabilities in npm packages. These campaigns bypass traditional security measures and persist within compromised systems by leveraging Node.js' cross-platform capabilities. Organizations must enhance monitoring, update dependencies, and educate users to defend against these evolving threats.
3. Midnight Blizzard Targets European Embassies
Midnight Blizzard, a Russian state-sponsored espionage group, initiated a spear-phishing campaign targeting diplomatic entities across Europe. This new campaign introduces a malware loader called GrapeLoader and a variant of the WineLoader backdoor. The phishing emails, impersonating the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, contain a malicious link that triggers the download of a ZIP archive with a PowerPoint executable and the GrapeLoader payload. Once executed, GrapeLoader stealthily collects system information, modifies the Windows Registry, and downloads WineLoader.
Click here for more alerts!
💥 Cyber Incidents
4. 4chan Hack Leaks Moderator and User Data
On Tuesday, 4chan was hacked, leading to the site's intermittent downtime. Leaked screenshots showed the back end of the site, including sensitive information about moderators, janitors, and their roles. The data breach exposed personal information from 4chan Pass subscribers who paid for special privileges. A janitor confirmed the leaks, expressing concern over the magnitude of the breach and its potential impact on 4chan's continued operation amid the site's known links to extremist and alt-right movements.
5. UK Minister Powell X Account Hacked for Scam
UK Government minister Lucy Powell's X account was hacked to promote a fraudulent cryptocurrency. The hacker posted misleading content about the "$HCC" coin, claiming it was a "community-driven digital currency." Powell's office confirmed the breach and acted quickly to secure the account. Similar attacks on high-profile figures like BBC's Nick Robinson highlight the growing cybercrime trend of hijacking social media accounts for scam promotions.
6. Jemeppe sur Sambre Suffers Cyberattack
On April 10, 2025, the municipality of Jemeppe-sur-Sambre, Belgium, and it's public center became victims of a significant cyberattack. The attackers infiltrated both the municipal services and the local social assistance center, disrupting their operations. Authorities reported that sensitive data and critical systems were compromised, with the attack affecting communication channels, financial services, and personal data. As a result, the local government has taken urgent measures to secure systems, investigate the extent of the breach, and mitigate the potential damage to public services and residents.
Click here for more incidents!
📢 Cyber News
7. MITRE Faces End of CVE Program Contract
MITRE’s management of the CVE program, which tracks cybersecurity vulnerabilities, is at risk as its contract with the U.S. government nears expiration on April 16. The expiration of funding from the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) will halt new CVE additions and potentially shut down the program’s website. The CVE system is critical for cybersecurity professionals, vendors, and government agencies worldwide, supporting vulnerability identification and mitigation efforts. Experts have raised alarms, fearing that a disruption could lead to a national security issue, particularly for critical infrastructure and incident response operations.
8. China Accuses NSA Employees of Cyberattacks
China has accused three alleged employees of the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) of carrying out cyberattacks during the Asian Winter Games in February. The public security bureau in Harbin stated that the attackers were linked to the NSA’s Office of Tailored Access Operations. These cyberattacks reportedly targeted registration, arrival management, and competition entry platforms, along with critical infrastructure like energy, transportation, telecommunications, and defense research in Heilongjiang province. While such accusations are not new, this marks the first time China has named specific individuals and provided detailed allegations about the incident.
9. LabHost Phishing Ringleader Jailed for Fraud
Zak Coyne, 24, was sentenced to eight and a half years in prison for running LabHost, a phishing site. The platform targeted over one million victims worldwide, defrauding them of £100 million through fraudulent payment sites. LabHost operated as a subscription service, enabling scammers, many without technical expertise, to create convincing fake websites. These scammers stole sensitive personal information, including bank details and PIN codes, from victims, with at least 70,000 victims in the UK alone. The site was taken down in April 2024 following a global law enforcement operation
Click here for more news!
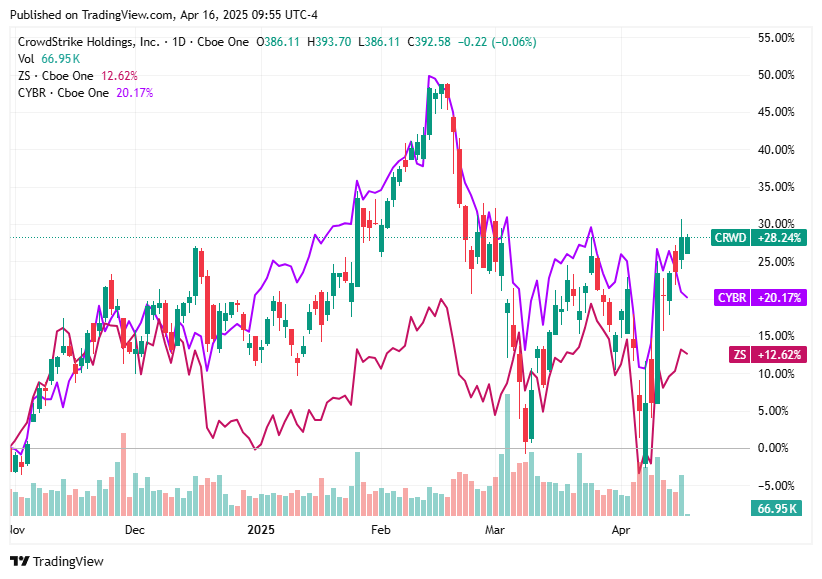
📈Cyber Stocks
💡 Cyber Tip
Watch Out for Malware Delivered via Node.js in Legit Software Packages
Cybercriminals are increasingly hiding malware in Node.js applications by exploiting open-source npm packages and using techniques like malvertising and supply chain attacks.
✅ Actions You Should Take:
Audit dependencies – Regularly scan and verify all open-source packages used in your applications.
Use trusted sources – Only download Node.js packages from reputable sources and maintain strict version control.
Monitor system behavior – Set up anomaly detection to flag unusual activity in systems using Node.js.
Why it matters: These attacks can bypass traditional security tools and infect systems cross-platform, making them especially dangerous for developers and enterprises relying on JavaScript environments.
📚 Cyber Book
The Hacker Playbook: Practical Guide to Penetration Testing by Peter Kim
📊 Cyber Poll
Copyright © 2025 CyberMaterial. All Rights Reserved.
Follow CyberMaterial on:
Substack, LinkedIn, Twitter, Reddit, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and Medium.