Cyber Briefing: 2025.04.15
The cybersecurity updates for today highlight ResolverRAT, BPFDoor, Teams malware, the Hertz and DaVita breaches, IAF GPS spoofing, Meta’s AI training, SSL/TLS changes, and breach laws in Queensland.
Listen to our podcast here!
Welcome to Cyber Briefing, the newsletter that informs you about the latest cybersecurity advisories, alerts, incidents and news every weekday.
First time seeing this?
👉 What's the latest in the cyber world today?
🚨 Cyber Alerts
1. ResolverRAT Targets Healthcare and Pharma
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered ResolverRAT, a sophisticated remote access trojan targeting healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors. Delivered through phishing emails, the malware exploits fear-based lures and DLL side-loading techniques to initiate execution. Once activated, ResolverRAT uses advanced in-memory execution, encryption, and compression to avoid detection and persist on the victim’s system. The malware is equipped with a multi-layered command-and-control infrastructure that rotates IPs and uses custom protocols, ensuring that it remains undetected while exfiltrating sensitive data.
2. BPFDoor Uses Reverse Shell for Access
BPFDoor, a sophisticated backdoor malware, has been actively targeting organizations in Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. By using Berkeley Packet Filtering technology, it monitors network traffic at the kernel level, staying hidden from conventional security measures. Deployed by the Earth Bluecrow group, this malware is used for long-term cyberespionage in sectors like telecommunications, finance, and retail. Its ability to avoid detection through reverse shell connections and stealthy processes makes BPFDoor a highly effective tool for persistent, undetected access to compromised systems.
3. Hackers Use Teams Chats to Deliver Malware
A sophisticated attack using Microsoft Teams chats has emerged, targeting Windows PCs. Cybersecurity firm ReliaQuest reported that the attack, linked to Storm-1811, began in March 2025. The attackers impersonate IT support staff through fraudulent Microsoft 365 accounts, tricking employees into running malicious software. This campaign uses novel techniques like TypeLib COM hijacking and PowerShell backdoors to maintain persistent access, making detection difficult.
💥 Cyber Incidents
4. Hertz Confirms Data Breach Exposing Info
Hertz Corporation confirmed a data breach involving customer data stolen through a zero-day vulnerability in Cleo’s platform. The breach impacted customers from Hertz, Thrifty, and Dollar brands, exposing sensitive details like names, contact information, and credit card data. The Clop ransomware gang, which has targeted other secure file transfer platforms before, claimed responsibility for the breach. Hertz is offering impacted customers free identity monitoring services and urges vigilance against fraud.
5. DaVita Ransomware Attack Disrupts Operations
On April 12, 2025, DaVita, a major kidney dialysis provider, confirmed it was targeted by a ransomware attack. The attack encrypted portions of the company’s network, leading to disruptions in some internal operations. Despite these issues, DaVita assured the public that patient care across its 2,600 dialysis centers continued uninterrupted. An investigation is ongoing to determine the full scope of the breach, and concerns remain about the potential theft of patient data, a common tactic in ransomware incidents.
6. GPS Spoofing Targets Indian Air Force
During Operation Brahma’s relief mission in Myanmar, an Indian Air Force (IAF) C-130J aircraft faced a GPS spoofing attack. The attack, which misled the aircraft's navigation system, occurred while the aircraft was flying over earthquake-hit Myanmar. Pilots quickly switched to the internal navigation system (INS) to maintain safe navigation and avoid potential mishaps. This was during India's humanitarian mission following the devastating 7.7 magnitude earthquake that struck Myanmar, leaving over 3,600 dead and thousands injured.
📢 Cyber News
7. Meta Resumes AI Training with Public Data
Meta has resumed training its artificial intelligence models using publicly shared data from adult users in the European Union. This decision comes after a year-long pause following concerns raised by Irish regulators over data protection. The AI training will utilize data such as posts, comments, and interactions with Meta’s AI across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger. However, private messages and data from users under 18 will not be included. The European Data Protection Board recently approved the rollout, with Meta informing users about the data collection through notifications and offering an opt-out option.
8. SSL TLS Certificate Lifespan Cut to 47 Days
The CA/Browser Forum has voted to shorten the lifespan of SSL/TLS certificates significantly over the next four years. Starting in March 2026, the lifespan will drop to 200 days, followed by a reduction to 100 days in March 2027. By March 2029, certificates will only be valid for 47 days. This decision, driven by security concerns, aims to reduce risks associated with outdated certificates and compromised credentials, encouraging companies to automate certificate renewals and making the entire ecosystem more secure and efficient.
9. Queensland Introduces Data Breach Law
Queensland’s new data breach notification law will take effect on July 1, 2025. The Information Privacy and Other Legislation Amendment Act 2023 mandates that agencies notify the Office of the Information Commissioner Queensland (OICQ) about eligible data breaches. The law requires agencies to report unauthorized access, loss, or disclosure of personal information if it poses a risk of serious harm. The new regulation aims to enhance transparency and ensure better protection of personal data.
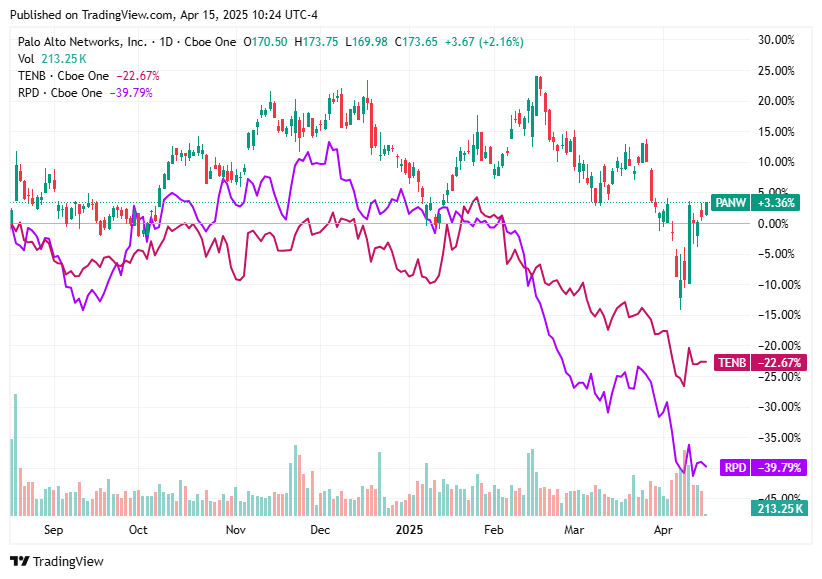
📈Cyber Stocks
💡 Cyber Tip
Beware of Malware Hidden in Microsoft Teams Chats
Hackers are now using fake Microsoft Teams accounts to impersonate IT staff and trick employees into installing malware through chat messages.
✅ Actions You Should Take:
Verify contacts – Always confirm unexpected IT requests via a known internal channel before taking action.
Limit Teams permissions – Restrict external messaging capabilities to prevent fake accounts from reaching staff.
Train employees – Conduct phishing simulation training focused on collaboration platforms like Teams and Slack.
Why it matters: These attacks bypass email security and exploit trust in internal tools, making them harder to detect and easier to fall for, especially in remote or hybrid work environments.
📚 Cyber Book
Cybersecurity for Dummies by Joseph Steinberg
📊 Cyber Poll
Copyright © 2025 CyberMaterial. All Rights Reserved.
Follow CyberMaterial on:
Substack, LinkedIn, Twitter, Reddit, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and Medium.