Cyber Briefing: 2025.07.25
Critical RCE flaws patched by Sophos and SonicWall; CastleLoader and Koske malware emerge; Amazon AI bot hacked; APTs target Tibetans; Steam malware, Jetflicks jail, Proton AI
🎉 Cyber Briefing Referral Giveaway Is Live!
We’re growing quickly on Substack, and now you can help spread the word and earn rewards.
Here’s what you can win by participating:
🔹 10 referrals: Newsletter shoutout
🔹 25 referrals: One-year free subscription
🔹 50 referrals: Cybersecurity consultation
🔹 Top referrer (100+ referrals; see rules): $100 gift card
This is our way of saying thank you for helping build a smarter cyber community.
👉 What's going on in the cyber world today?
Welcome to Cyber Briefing, the newsletter that informs you about the latest cybersecurity advisories, alerts, incidents and news every weekday.
First time seeing this? Please Subscribe
🚨 Cyber Alerts
1. Sophos, SonicWall Patch Critical RCE Bugs
Sophos and SonicWall have announced critical security flaws in their Firewall and Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series appliances, respectively. These vulnerabilities could allow attackers to execute remote code, and both companies have released patches to address the issues.
2. CastleLoader Uses Clickfix on Windows
A newly identified malware, CastleLoader, has emerged as a significant threat, using sophisticated phishing and social engineering to trick users into running malicious PowerShell scripts. Functioning as a distribution platform, it has successfully infected hundreds of high-value targets, including U.S. government entities, to deploy various information stealers and remote access trojans.
3. Koske Malware Hides in Panda Images
A new, sophisticated Linux malware named Koske, which researchers suspect was developed with AI, uses seemingly harmless JPEG images of pandas to deploy cryptocurrency miners directly into system memory. This threat establishes a stealthy foothold by executing a rootkit and a shell script from memory, profiling the system to efficiently mine over 18 different coins while hiding its presence.
For more alerts, click here!
💥 Cyber Incidents
4. Hackers Target Amazon’s AI Code Bot
A security breach exposed vulnerabilities in Amazon's AI infrastructure after hackers injected malicious computer-wiping commands into its AI coding assistant, 'Q'. The incident, executed via a simple GitHub pull request, highlights the growing threat of prompt injection attacks on AI systems and the inadequacy of traditional security measures.
5. APTs Use Fake Dalai Lama Apps to Spy
A China-nexus cyber espionage group launched two campaigns, "Operation GhostChat" and "Operation PhantomPrayers," against the Tibetan community by using fraudulent websites themed around the Dalai Lama's 90th birthday. These attacks lured victims into downloading trojanized applications, ultimately installing the powerful Gh0st RAT backdoor to conduct surveillance and steal information.
6. Infostealer Hidden in Steam Game
A threat actor named EncryptHub has compromised the early-access game "Chemia" on Steam, embedding info-stealing malware within its files. Unsuspecting players who download the title are infected with malware that silently harvests sensitive data, including account credentials and cryptocurrency wallet information.
For more incidents, click here!
📢 Cyber News
7. Jetflicks Operator Sentenced to 7 Years
The ringleader of the Jetflicks illegal streaming service, Kristopher Lee Dallmann, has been sentenced to seven years in prison for running a massive piracy operation that generated millions in profits. Operating for 12 years, the service used automated software to pirate over 183,000 TV episodes and 10,500 movies, causing an estimated $37.5 million in damages to copyright holders before its shutdown by the FBI in 2019.
8. Proton Launches Encrypted AI Assistant
Proton has introduced Lumo, a new privacy-first AI assistant designed to protect user data by not logging conversations or using them for model training. Built on open-source LLMs and encryption, the tool reflects the Swiss company's non-profit mission, offering a transparent and secure alternative to mainstream AI services.
9. Brave Blocks Windows Recall Screenshot
Brave Software is proactively blocking Microsoft's Windows Recall from capturing user activity within its privacy-focused browser by default. This move aims to protect users' sensitive Browse history from being stored in what Brave considers a "persistent database" that is vulnerable to abuse.
For more news, click here!
📈Cyber Stocks
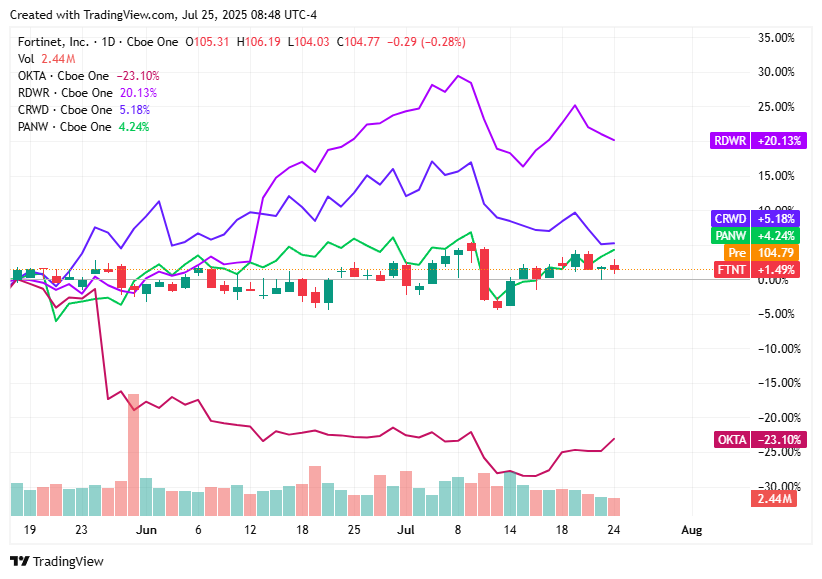
Cybersecurity stocks moved cautiously on Friday, July 25, 2025, as investor sentiment reflected concerns over high valuations, AI investment momentum, institutional positioning, and escalating geopolitical cyber threats.
Palo Alto Networks (PANW) rose modestly to $199.22, supported by investor confidence in its AI-driven platform and alignment with U.S. federal cybersecurity initiatives.
Okta (OKTA) was unchanged at $95.65, as investors balanced strong Q2 earnings with cautious analyst guidance and elevated valuation levels, while institutional trading volume surged over 42 percent.
Radware (RDWR) edged down to $28.80, slipping slightly amid broader sector consolidation and uncertainty ahead of its upcoming earnings release, following earlier investor enthusiasm.
CrowdStrike (CRWD) declined 2.1% to $461.52, driven by profit-taking and valuation concerns, despite continued optimism about its AI-fueled demand and future deal growth.
Fortinet (FTNT) ticked up to $105.06, benefiting from stable recurring revenue and its reputation as a defensive cybersecurity play amid rising global cyber threats and increased government spending.
💡 Cyber Tip
New Linux Malware Hides in Innocent-Looking Panda Images
Researchers have uncovered a stealthy Linux malware called Koske that uses real JPEG images of pandas to hide and deliver its payload. These images double as executable scripts that deploy a rootkit and a cryptocurrency miner directly into system memory. Once active, the malware profiles the system’s hardware to mine over 18 cryptocurrencies while concealing its presence with advanced evasion techniques.
✅ What you should do:
Avoid running or downloading image files from untrusted or unfamiliar sources, even if they appear harmless.
Audit public-facing systems like JupyterLab to ensure they are properly secured and not exposed online.
Monitor for unusual CPU/GPU usage that may indicate hidden mining activity.
Use Linux security tools that detect in-memory execution, rootkit behavior, and unauthorized cron jobs or services.
Regularly check for suspicious scripts or binaries in temporary directories and system startup configurations.
🔒 Why this matters:
Koske uses sophisticated techniques to bypass file-based detection and execute directly in memory. Its ability to adapt, remain hidden, and use everyday file types like images highlights the need for deeper inspection and stronger controls, especially in Linux environments handling sensitive workloads.
📚 Cyber Book
All the Ghosts in the Machine: The Digital Afterlife of your Personal Data by Elaine Kasket
That concludes today’s briefing . You can check the top headlines here!
Copyright © 2025 CyberMaterial. All Rights Reserved.
Follow CyberMaterial on:
Substack, LinkedIn, Twitter, Reddit, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and Medium.